As discussed in the first blog in this three-part series, key factory shutdowns and general shifts in the X-Ray imaging market have lead to Image Intensifier (II)-CCD RIUs going obsolete. As CCD obsolescence becomes more prevalent in Healthcare and the dynamic imaging X-Ray market, the need to find alternatives is imminent. There are three flat panel detector technologies in the market, all vying to take CCD’s place as the key market alternative. These are Amorphous Silicon (aSi), CMOS, and the newly emerging Indium gallium zinc oxide (IGZO).
CMOS X-Ray Detectors
Over the past decade CMOS flat panel technology has been seeing a strong growth in the X-Ray dynamic imaging market. These flat panel detectors work via the X-ray energy reaching a scintillator and passing through micro-lenses to the CMOS sensor, which creates an image. This allows for key features that make it a viable alternative to Image Intensifier (II) based RIU’s with CCD image sensors (II-CCD RIUs). CMOS flat panel detectors support signal detection with low read noise (due to active pixel designs), allowing low(er) dose X-ray imaging. Their ability to utilize small pixels (e.g. 50um and even less) and short readout times support high resolution imagers in small dimension panels with high acquisition speeds. While CMOS detectors have strong performance characteristics (resolution, speed and sensitivity), the cost of technology becomes high for larger panels (>6”). This is due to using multiple cut-outs of sensor tiles from single wafers which contributes to cost build-up when stitched together in these large panels (especially 12” and 17” formats).
aSi X-Ray Detectors
A second alternative to the II-CCD RIUs are Amorphous Silicon flat panel detectors, which over the past 2 decades, have become dominantly used in medical X-Ray imaging for both static and dynamic applications. Amorphous Silicon (aSi) is a key technology in entry level displays that are produced in high volumes. This benefits cost effectiveness when used in X-Ray detectors especially in larger panels such as 12” and 17” formats. In addition, they are better suited for high dose exposures than CMOS detectors and II-CCD RIUS. Although boasting a lower detector cost, aSi has a few drawbacks that would limit its uses in dynamic X-ray imaging to more niche situations. aSi does not perform as well in low dose exposures compared to II-CCD RIU’s or CMOS detectors, is slower in pixel readout speeds, and cannot support the smaller pixels as may be used in CMOS detectors, which restricts very high resolutions. These factors limit the applicable combinations of resolution and frame speed possible in dynamic imaging applications.
IGZO X-Ray Detectors
The third alternative on the market are the recent Indium gallium zinc oxide (IGZO) flat panel detectors. Like aSi they also use photodiodes but combine these with IGZO TFT’s instead of aSi TFT’s. IGZO TFT’s can be made smaller than aSi TFT’s and offer significantly improved switching performances. As a consequence, pixels become more sensitive (lower noise), can provide faster readout, and detector panel resolution can be further increased. IGZO panels are also just as available in cost effective and versatile options as the aSi panels with sizes ranging from 6” to 17” for medical applications. Unlike the aSi panels, they can acquire a usable image at equal or lower x-ray dose at faster acquisition speeds and with higher resolution. Performance wise, IGZO detectors are second best to CMOS detectors, but their expected price point – especially in larger detector formats – puts them in a promising position to replace the obsolete II-CCD RIU’s.
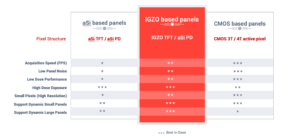
As stated in a 2019 research report by Yole Development, “IGZO have long been seen as a potential ideal ‘high performance/low-cost’ TFT technology” but they also mention a key barrier is lack of supply chain readiness. However, multiple display manufacturers have begun over the last year to introduce and produce IGZO panels for X-Ray detection. This new market availability positions IGZO as an interesting alternative to II-CCD RIUs over aSi and CMOS detectors. For the next blog in this series, we will explore important things to consider when transitioning from CCD RIU’s to Flat Panel Detector technology in Mobile C-arms.
 English
English 日本語
日本語 简体中文
简体中文



Thanks for nicely detailing products.
Please let us know potential manufacture .We are manufacturer of C Arm with CCD base camera.
Dear Ajit, Mr Bose,
Sorry for our delayed reply. In India, Adimec closely works together with Global Imaging who represents Adimec. I will forward your interest to Mr Ashish Arora of GI. I am sure he will follow-up.